Technology at Newport News Public Schools

Wayne A. Santos, II, MBA
Executive Director, Technology
Technology Service Center
(757) 881-5461 x.12411
Phishing
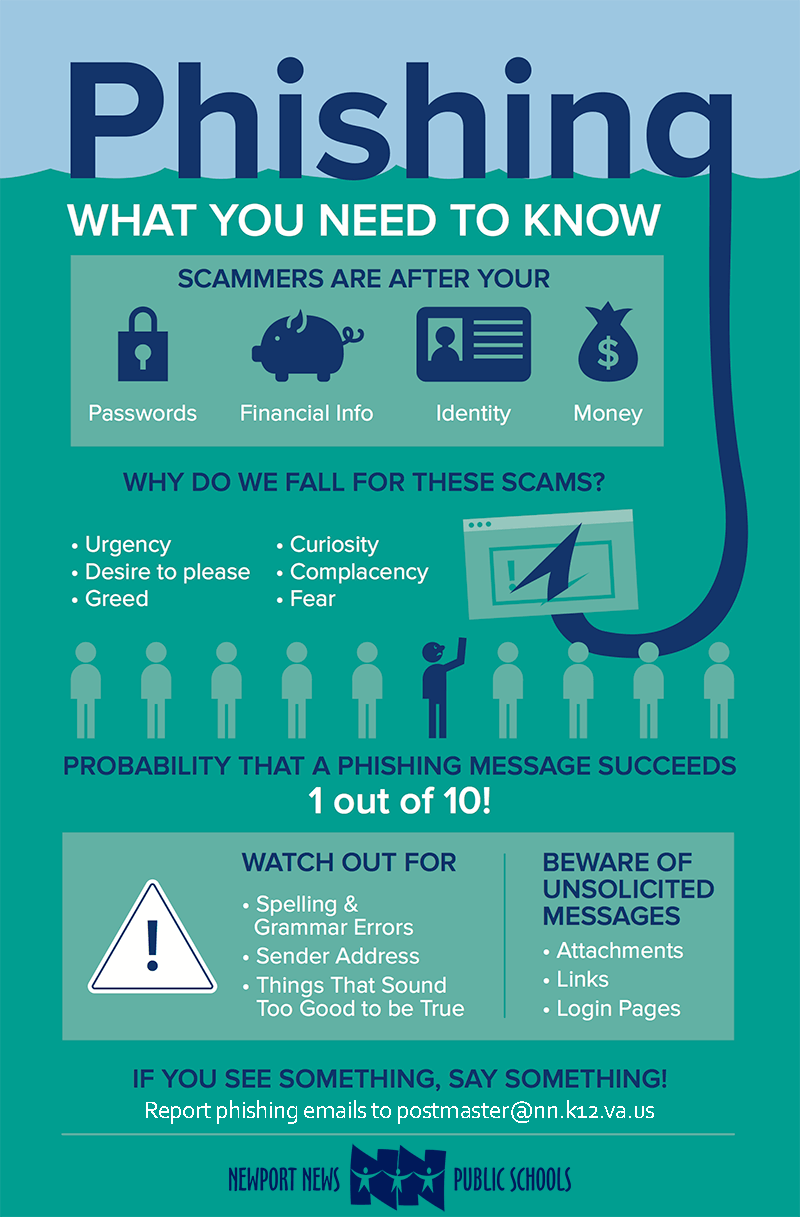
Phishing is a cybercrime in which a target or targets are contacted by email, telephone or text message by someone posing as a legitimate institution to lure individuals into providing sensitive data such as banking and credit card details, personally identifiable information (PII), student information and passwords.
The information gained by attackers is then used to access important accounts. This can result in identity theft and financial loss.
Types of Phishing
-
Clone phishing: A legitimate, and previously delivered, email containing an attachment or link has had its content and recipient addresses taken and used to create an almost identical or cloned email. The attachment or link within the email is replaced with a malicious version and then sent from an email address spoofed to appear to come from the original sender.
-
Spear phishing: Phishing attempts directed at specific individuals or companies have been termed spear phishing.
-
Whaling: Attacks have been directed specifically at senior executives and other high-profile targets within businesses (CEO, Director, etc.)
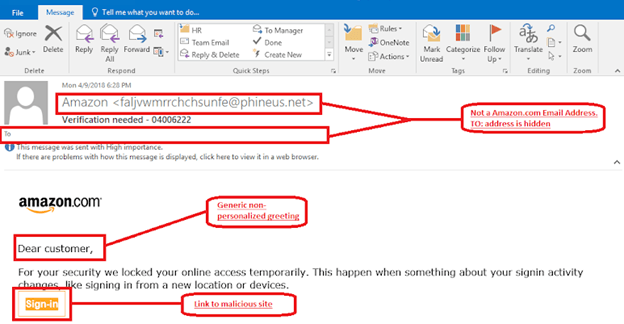
What does a phishing email look like?
Steps you can take to prevent phishing
-
Check the spelling of the URLs in email links before you click or enter sensitive information
-
Watch out for URL redirects where you're sent to a different website with identical design
-
If a message came from one of your friends or co-workers, remember that they could also have been fooled or hacked. Remain cautious in any situation. Even if a message seems friendly, treat links and attachments with suspicion.
-
Hyperlinks, most likely, will be incorrect. Messages or the Subject will contain spelling mistakes, or they can redirect you to a different place.
Report suspicious email
Not sure if it's a phishing email? Contact the Technology Service Center or forward the email to [email protected].
Infographic: Protect Your Computer from Malware
Adapted and used with permission from security.stanford.edu.